Vue.js与ElementUI搭建无限级联层级表格组件
前言
今天,回老家了。第一件事就是回家把大屏安排上,写作的感觉太爽了,终于可以专心地写文章了。我们今天要做的项目是怎么样搭建一个无限级联层级表格组件,好了,多了不多说,赶快行动起来吧!
项目一览
到底是啥样子来?我们来看下。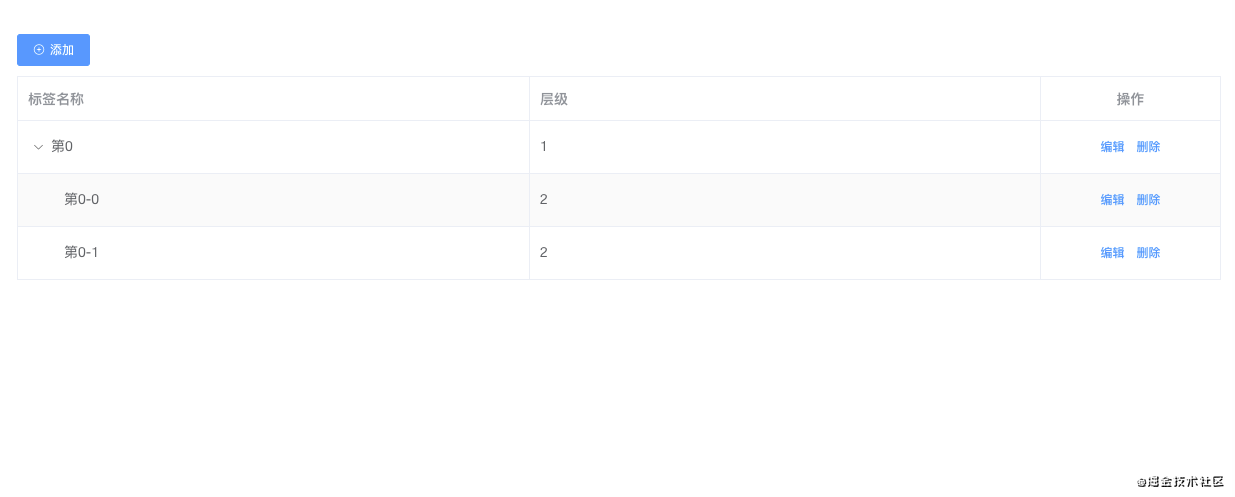
正如你所看到的那样,这个组件涉及添加、删除、编辑功能,并且可以无限级嵌套。那么怎样实现的?我们来看下。
源码
直接给出源码,就是这么直接。
<template>
<div class="container">
<el-button
type="primary"
size="small"
@click="handleCreate"
icon="el-icon-circle-plus-outline"
style="margin: 10px 0"
>添加</el-button
>
<el-table
:data="tableData"
style="width: 100%; margin-bottom: 20px"
border
row-key="value"
stripe
size="medium"
:tree-props="{ children: 'children' }"
>
<el-table-column prop="label" label="标签名称"> </el-table-column>
<el-table-column prop="location" label="层级"> </el-table-column>
<el-table-column label="操作" :align="alignDir" width="180">
<template slot-scope="scope">
<el-button
type="text"
size="small"
@click="handleUpdate(scope.row)"
>编辑</el-button
>
<el-button
type="text"
size="small"
@click="deleteClick(scope.row)"
>删除</el-button
>
</template>
</el-table-column>
</el-table>
<el-dialog
:title="textMap[dialogStatus]"
:visible.sync="dialogFormVisible"
width="30%"
>
<el-form
ref="dataForm"
:rules="rules"
:model="temp"
label-position="left"
label-width="120px"
style="margin-left: 50px"
>
<el-form-item
label="层级:"
prop="location"
v-if="dialogStatus !== 'update'"
>
<el-select
v-model="temp.location"
placeholder="请选择层级"
@change="locationChange"
size="small"
>
<el-option
v-for="item in locationData"
:key="item.id"
:label="item.name"
:value="item.id"
/>
</el-select>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item
v-if="sonStatus && dialogStatus !== 'update'"
label="子位置:"
prop="children"
>
<el-cascader
size="small"
:key="isResouceShow"
v-model="temp.children"
placeholder="请选择子位置"
:label="'label'"
:value="'value'"
:options="tableData"
:props="{ checkStrictly: true }"
clearable
@change="getCasVal"
></el-cascader>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="标签名称:" prop="label">
<el-input
v-model="temp.label"
size="small"
autocomplete="off"
placeholder="请输入标签名称"
></el-input>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
<div slot="footer" class="dialog-footer">
<el-button @click="dialogFormVisible = false" size="small">
取消
</el-button>
<el-button
type="primary"
size="small"
@click="
dialogStatus === 'create' ? createData() : updateData()
"
>
确认
</el-button>
</div>
</el-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Tag',
data() {
return {
alignDir: 'center',
textMap: {
update: '编辑',
create: '添加',
},
dialogStatus: '',
dialogFormVisible: false,
temp: {},
isResouceShow: 1,
sonStatus: false,
casArr: [],
idx: '',
childKey: [],
rules: {
location: [
{
required: true,
message: '请选择层级',
trigger: 'blur',
},
],
label: [
{ required: true, message: '请输入名称', trigger: 'blur' },
],
children: [
{
required: true,
message: '请选择子位置',
trigger: 'blur',
},
],
},
locationData: [
{
id: '1',
name: '顶',
},
{
id: '2',
name: '子',
},
],
tableData: [
{
tagId: '1', // 标签id
label: '第0', // 标签名称
parent: '', // 父级名称
location: '1', // 层级
value: '0', // 标识位
children: [
{
tagId: '1', // 子标签id
childKey: ['0', '0'], // 子标识位
label: '第0-0',
parent: '第0',
location: '2',
value: '0-0',
children: [],
},
{
tagId: '2', // 子标签id
childKey: ['0', '1'],
label: '第0-1',
parent: '第0',
location: '2',
value: '0-1',
children: [],
},
],
},
]
};
},
methods: {
// 递归寻找同级
findSameTable(arr, i, casArr) {
if (i == casArr.length - 1) {
return arr;
} else {
return this.findTable(
arr[casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1)].children,
(i += 1),
casArr
);
}
},
// 寻找父级
findTable(arr, i, casArr) {
if (i == casArr.length - 1) {
let index = casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1);
return arr[index];
} else {
return this.findTable(
arr[casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1)].children,
(i += 1),
casArr
);
}
},
// 递归表格数据(添加)
find(arr, i) {
if (i == this.casArr.length - 1) {
return arr[this.casArr[i].substr(this.casArr[i].length - 1, 1)]
.children;
} else {
return this.find(
arr[this.casArr[i].substr(this.casArr[i].length - 1, 1)]
.children,
(i += 1)
);
}
},
// 递归表格数据(编辑)
findSd(arr, i, casArr) {
if (i == casArr.length - 1) {
let index = casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1);
return arr.splice(index, 1, this.temp);
} else {
return this.findSd(
arr[casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1)].children,
(i += 1),
casArr
);
}
},
// 递归寻找同步名称
findLable(arr, i, casArr) {
if (i == casArr.length - 1) {
let index = casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1);
return arr[index];
} else {
return this.findLable(
arr[casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1)].children,
(i += 1),
casArr
);
}
},
// 同步子名称
useChildLable(arr) {
if (arr !== []) {
arr.forEach((item) => {
item.parent = this.temp.label;
});
}
},
// 递归表格数据(删除)
findDel(arr, i, item) {
let casArr = item.childKey;
if (i == casArr.length - 2) {
let index = casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1);
arr[index].children.forEach((it, ix, arrs) => {
if (it == item) {
return arrs.splice(ix, 1);
}
});
} else {
return this.findDel(
arr[casArr[i].substr(casArr[i].length - 1, 1)].children,
(i += 1),
item
);
}
},
// 置空
resetTemp() {
this.temp = {};
},
// 打开添加
handleCreate() {
this.resetTemp();
this.dialogFormVisible = true;
this.dialogStatus = 'create';
this.$nextTick(() => {
this.$refs['dataForm'].clearValidate();
});
},
// 添加
createData() {
this.$refs['dataForm'].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
if (this.sonStatus == false) {
this.temp.value = String(this.tableData.length);
const obj = Object.assign({}, this.temp);
obj.children = [];
obj.parent = '';
this.tableData.push(obj);
this.$message({
type: 'success',
message: '添加成功',
});
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
} else {
let arr = this.find(this.tableData, 0);
this.temp.value =
String(this.casArr[this.casArr.length - 1]) +
'-' +
String(arr.length);
delete this.temp.children;
const obj = Object.assign({}, this.temp);
obj.children = [];
obj.childKey = [...this.casArr, String(arr.length)];
obj.parent = this.findTable(
this.tableData,
0,
this.casArr
).label;
if (this.temp.location === '2') {
obj.location = String(
[...this.casArr, String(arr.length)].length
);
}
arr.push(obj);
this.$message({
type: 'success',
message: '添加成功',
});
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
});
},
// 打开更新
handleUpdate(row) {
console.log(row);
row.value.length != 1
? (this.sonStatus = true)
: (this.sonStatus = false);
this.temp = Object.assign({}, row); // copy obj
if (row.childKey) {
this.childKey = row.childKey;
this.idx = row.childKey[row.childKey.length - 1];
} else {
this.idx = row.value;
}
console.log(this.idx);
this.dialogStatus = 'update';
this.dialogFormVisible = true;
this.$nextTick(() => {
this.$refs['dataForm'].clearValidate();
});
},
// 更新
updateData() {
this.$refs['dataForm'].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
if (this.temp.location === '1') {
console.log(this.temp);
this.tableData.splice(this.idx, 1, this.temp);
this.useChildLable(this.tableData[this.idx].children);
this.$message({
type: 'success',
message: '编辑成功',
});
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
} else {
this.findSd(this.tableData, 0, this.childKey);
this.useChildLable(
this.findLable(this.tableData, 0, this.childKey)
.children
);
this.$message({
type: 'success',
message: '编辑成功',
});
this.dialogFormVisible = false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
});
},
// 删除父级节点
deleteParent(item) {
this.tableData.forEach((it, ix, arrs) => {
if (it == item) {
return arrs.splice(ix, 1);
}
});
},
// 删除
deleteClick(item) {
this.$confirm(`此操作将删除该标签, 是否继续?`, '提示', {
confirmButtonText: '确定',
cancelButtonText: '取消',
type: 'warning',
})
.then(() => {
if (item.children.length != 0) {
this.$message.warning({
message: '请删除子节点',
duration: 1000,
});
} else {
++this.isResouceShow;
if (item.value.length == 1) {
this.deleteParent(item);
this.$message({
type: 'success',
message: '删除成功',
});
} else {
this.findDel(this.tableData, 0, item);
this.$message({
type: 'success',
message: '删除成功',
});
}
}
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
this.$message({
type: 'info',
message: '已取消删除',
});
});
},
// 是否显示次位置
locationChange(v) {
if (v == 2) {
this.sonStatus = true;
} else {
this.sonStatus = false;
}
},
// 获取次位置
getCasVal(v) {
this.casArr = v;
},
},
};
</script>
代码可以直接拿来用,但是要注意事先要安装下ElementUI框架。无限层级的核心算法是递归算法,掌握了这一点,任何难题都可以解决。
下面,我们就这个项目来回顾下前端中的递归算法。
递归简而言之就是函数调用自己。递归算法中有两个条件:基线条件和递归条件。基线条件用于控制递归啥时候暂停,而递归条件是控制调用自己的方式。
最简单的一个例子是5的阶乘。
var func = function(i){
if(i === 1){
return 1;
}else{
return i*func(i-1);
}
}
func(5);
这样就很简单的实现了一个递归算法,我们将上述例子拆解下。
// 递
5*func(4);
5*4*func(3);
5*4*3*func(2);
5*4*3*2*func(1);
// 归
5*4*3*2*1;
5*4*3*2;
5*4*6;
5*24;
120
递归其实可以理解成两个操作递与归。可以这样比喻,比如你在做一道数学题时,有一个知识点你不懂,你需要查资料。但是,通过查资料你发现这个知识点中你又有另一个不明白的知识点,你又开始继续查,直到你没有不懂的知识点,这样递的操作已经完成。然后,你把已经查过的这些知识点又从尾到头复习了一遍,这样归的操作已经完成。最后,你明白了最初那个知识点。
作者:Vam的金豆之路
主要领域:前端开发
我的微信:maomin9761
微信公众号:前端历劫之路



 个人中心
个人中心 退出
退出




 分类导航
分类导航