MyBatis 学习笔记(二)MyBatis常用特性运用
概要
接上一篇MyBatis 学习笔记(一)MyBatis的简介与使用以及与其他ORM框架的比较,今天我们接着来学习MyBatis的一些常用特性,包括别名,类型处理器,动态SQL
如何使用MyBatis
在本小节,我将通过一个例子介绍MyBatis 中一些常用特性的运用,包括类型处理器,动态SQL等等。
别名
MyBatis 中有个比较好用的特性就是别名,这是为了减少在配置文件中配置实体类的全限定名的冗余。运用如下:
首先在MyBatis的配置文件中配置别名:
<!--别名处理-->
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.jay.chapter2.entity.Student" alias="Student"/>
</typeAliases>
然后,在需要使用该实体类的映射文件中进行添加即可。
<resultMap id="studentResult" type="Student">
//省略其他无关配置
</resultMap>
类型处理器的运用
在实际开发中,我们经常要对枚举类进行处理,例如,人的性别分为男,女,我们数据库中可能存的是0,1; 但是页面显示的话需要显示男,女,所以,我们在使用MyBatis时查询结果时就要通过转换器进行转换。
MyBatis 内置了很多类型处理器(typeHandlers),详细可以参考MyBatis官方文档,对枚举类的处理的是通过EnumTypeHandler和EnumOrdinalTypeHandler两个处理器来处理了,

但是其只能处理简单的枚举,例如:
public enum SexEnum {
MAN,
FEMALE,
UNKNOWN;
}
对于复杂的枚举类型,则不能处理。例如:
MAN("0", "男")
我们来查看源码分析下原因,我们以EnumTypeHandler为例来说明下。
public class EnumTypeHandler<E extends Enum<E>> extends BaseTypeHandler<E> {
private final Class<E> type;
public EnumTypeHandler(Class<E> type) {
if (type == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Type argument cannot be null");
}
this.type = type;
}
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, E parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
if (jdbcType == null) {
ps.setString(i, parameter.name());
} else {
ps.setObject(i, parameter.name(), jdbcType.TYPE_CODE);
}
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
String s = rs.getString(columnName);
return s == null ? null : Enum.valueOf(type, s);
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
String s = rs.getString(columnIndex);
return s == null ? null : Enum.valueOf(type, s);
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
String s = cs.getString(columnIndex);
return s == null ? null : Enum.valueOf(type, s);
}
}
分析上述源码,setNonNullParameter方法包装PreparedStatement进行SQL插值操作,设置的值是enum.name() ,即enum的toString() ,存储的枚举值的名称,而getNullableResult 方法返回的是Enum.valueOf(type, s)。而EnumOrdinalTypeHandler转换器也只能处理Int,String 类型。故我们需要自定义转换器来处理。分析MyBatis 源码我们可以得知,各个转换器都是继承BaseTypeHandler 基类的。为了实现代码的通用性,首先我们实现了一个枚举基类,然后定义一个通用的转换器。
枚举基类:
public interface BaseEnum<E extends Enum<?>, T> {
/**
* 真正与数据库进行映射的值
* @return
*/
T getKey();
/**
* 显示的信息
* @return
*/
String getValue();
}
在枚举记录中我们定义了两个通用的获取key和value的方法,接着我们定义 一个枚举类SexEnum来实现枚举基类
public enum SexEnum implements BaseEnum<SexEnum, String> {
MAN("0", "男"),
WEMAN("1", "女"),;
private String key;
private String value;
final static Map<String, SexEnum> SEX_MAP = new HashMap<>();
static {
for (SexEnum sexEnums : SexEnum.values()) {
SEX_MAP.put(sexEnums.key, sexEnums);
}
}
SexEnum(String key, String value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
@Override
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public static SexEnum getEnums(String key) {
return SEX_MAP.get(key);
}
}
接下来我们再来看看通用的转换器类。
public class GeneralEnumHandler<E extends BaseEnum> extends BaseTypeHandler<E> {
private Class<E> type;
private E[] enums;
public GeneralEnumHandler(Class<E> type) {
if (type == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Type argument cannot be null");
}
this.type = type;
//获取实现枚举基类所有的枚举类
this.enums = type.getEnumConstants();
if (enums == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(type.getSimpleName()
+ "does not represent an enum type.");
}
}
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement preparedStatement, int i, E e, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
if (jdbcType == null) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i, e.getKey());
} else {
//将枚举类的key,存入数据库中
preparedStatement.setObject(i, e.getKey(), jdbcType.TYPE_CODE);
}
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, String s) throws SQLException {
if (resultSet.wasNull()) {
return null;
}
Object key = resultSet.getObject(s);
return locateEnumsStatus(key);
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException {
if (resultSet.wasNull()) {
return null;
}
Object key = resultSet.getObject(i);
return locateEnumsStatus(key);
}
@Override
public E getNullableResult(CallableStatement callableStatement, int i) throws SQLException {
if (callableStatement.wasNull()) {
return null;
}
Object key = callableStatement.getObject(i);
return locateEnumsStatus(key);
}
/*
* 根据枚举类的key,获取其对应的枚举
* @param key
* @return
*/
private E locateEnumsStatus(Object key) {
if (key instanceof Integer) {
for (E anEnum : enums) {
if (anEnum.getKey() == key) {
return anEnum;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的枚举类型:" + key + ",请核对" + type.getSimpleName());
}
if (key instanceof String) {
for (E anEnum : enums) {
if (anEnum.getKey().equals(key)) {
return anEnum;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的枚举类型:" + key + ",请核对" + type.getSimpleName());
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("未知的枚举类型:" + key + ",请核对" + type.getSimpleName());
}
}
代码编写好之后,我们需要在所使用的Mapper映射文件中进行必要的配置。
<result property="sexEnum" column="sex"
typeHandler="com.jay.chapter2.Handler.GeneralEnumHandler"/>
最后我们来编写一个测试类来处理一下
public class SimpleMyBatis3Test {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
/**
*
*/
@Before
public void setUp() {
String config = "chapter2/mybatis-cfg.xml";
try {
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(config);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectStudent() {
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Student2Mapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(Student2Mapper.class);
Student student = mapper.selectStudentById(1);
System.out.println("------>返回结果"+student.toString());
}
}
测试结果如下:

动态SQL的使用
MyBatis的强大特性之一便是它的动态SQL,主要是处理 根据不同条件拼接SQL语句,例如拼接时添加必要的空格,去掉列表中的最后一列的逗号,MyBatis的动态SQL 元素是基于OGNL的表达式。
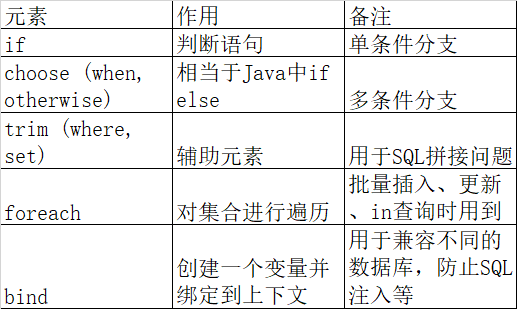
详细的运用可以参考
MyBatis官方文档
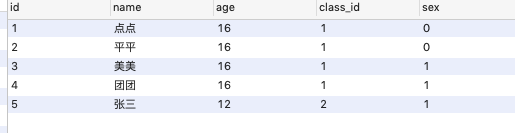
下面以一个例子作为一个示范。自此处我们有一张Student表,测试数据如下:
首先,我们在mybatis-cfg.xml配置好映射文件
<!-- 加载映射文件-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="chapter2/xml/Student3Mapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
然后,我们编写映射文件,将运用相关的动态SQL表达式。
mapper namespace="com.jay.chapter2.mapper.Student3Mapper">
<resultMap id="studentResult" type="com.jay.chapter2.entity.Student">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<result property="sexEnum" column="sex"
typeHandler="com.jay.chapter2.Handler.GeneralEnumHandler"/>
</resultMap>
<!--运用where,if元素进行条件拼接-->
<select id="selectStudent" resultMap="studentResult">
SELECT * FROM student
<where>
<if test="id!=null">
id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="name!=null">
AND name like CONCAT('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
</where>
</select>
<!--运用foreach元素进行实现in查询-->
<select id="selectByIds" resultMap="studentResult">
SELECT * FROM student
<where>
<if test="ids!=null">
id IN
<foreach collection="ids" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="id">
#{id}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
<!--运用choose,when,otherwise元素实现多条件分支-->
<select id="selectByNameOrAge" resultMap="studentResult">
SELECT * FROM student
<where>
<choose>
<when test="name!=null">
AND name like CONCAT('%',#{name},'%')
</when>
<when test="age!=null">
AND age=#{age}
</when>
<otherwise>
1=1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
<!--运用set元素sql拼接问题-->
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="Student">
UPDATE student
<set>
<if test="name!=null">
name=#{name},
</if>
<if test="age!=null">
age=#{age},
</if>
</set>
<where>
id=#{id}
</where>
</update>
</mapper>
该动态SQL对应的DAO 接口如下:
public interface Student3Mapper {
/**
* 查询学生
* @param id
* @param name
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectStudent(@Param("id") Integer id,
@Param("name") String name);
/**
* 批量查询学生
* @param ids
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByIds(@Param("ids") List<Integer> ids);
/**
* @param name
* @param age
* @return
*/
List<Student> selectByNameOrAge(@Param("name") String name,
@Param("age") Integer age);
/**
* 更新学生记录
* @param student
* @return
*/
boolean updateStudent(Student student);
}
接口类和其对应的映射文件编写完成之后,接着我们来编写测试类进行测试下。
public class SimpleMyBatis3Test extends BaseMyBatisTest {
@Test
public void testSelectStudent() {
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Student3Mapper mapper = session.getMapper(Student3Mapper.class);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectStudent(1, null);
System.out.println("----》只传id返回结果"+students.toString());
List<Student> students1 = mapper.selectStudent(null, "平平");
System.out.println("----》只传name返回结果"+students1.toString());
}
@Test
public void testSelectByIds() {
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Student3Mapper mapper = session.getMapper(Student3Mapper.class);
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(2);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByIds(ids);
System.out.println("---->通过ids查询返回结果" + students.toString());
}
@Test
public void selectByNameOrAge() {
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Student3Mapper mapper = session.getMapper(Student3Mapper.class);
List<Student> students = mapper.selectByNameOrAge("美美", null);
System.out.println("---->selectByNameOrAge通过name查询返回结果" + students.toString());
List<Student> students1 = mapper.selectByNameOrAge(null, 1);
System.out.println("----->selectByNameOrAge通过age查询返回的结果" + students1.toString());
}
@Test
public void testUpdateStudent() {
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
Student3Mapper mapper = session.getMapper(Student3Mapper.class);
Student student = new Student();
student.setId(1);
student.setName("小伟");
student.setAge(29);
boolean result = mapper.updateStudent(student);
System.out.println("--->updateStudent更新结果" + result);
}
}
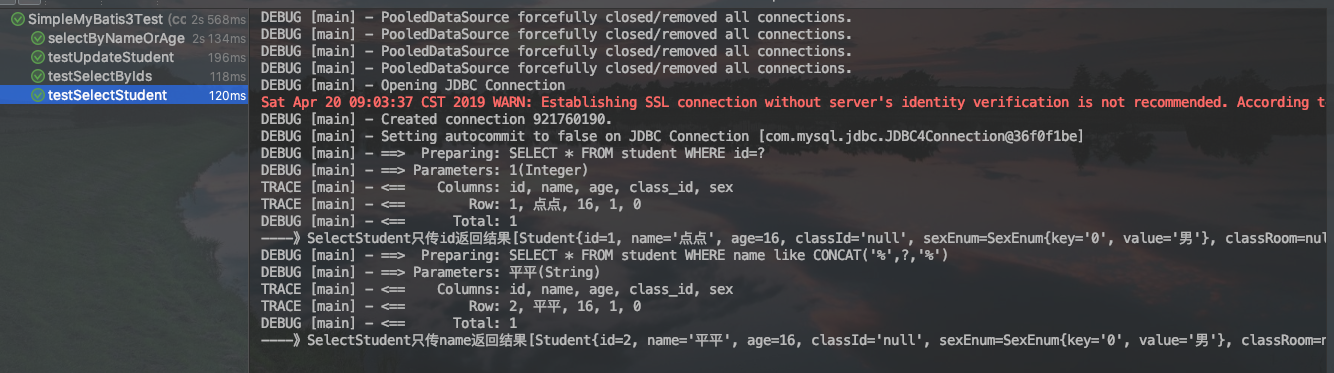
测试结果如下:
参考文献
MyBatis 3官方文档
mybatis枚举自动转换(通用转换处理器实现)
源代码
https://github.com/XWxiaowei/MyBatisLearn/tree/master/mybatisDemo
作者:码农飞哥
微信公众号:码农飞哥



 个人中心
个人中心 退出
退出




 分类导航
分类导航