用深度神经网络搭建马赛克神器,高清无码效果感人
=目录
1、项目背景
相信一提起马赛克这个东西,不少小伙伴都痛心疾首,虽然最近几年也频繁传出有在研发去除马赛克的软件,一直没有成品问世。不过最近一位程序员及经过不断努力终于完成了这款软件。
据悉这位程序员“deeppomf”用深度神经网络开发出了一个能抹去马赛克让原图重现的神奇程序:DeepCreamPy 。为了使这款软件达到更好的效果,作者在短短几个月内收集了超过10万张未打码的原图,但其中95%的图片他都没有仔细看过,只因为太过于浪费时间了。软件被上传分享后,在一周内被下载了500多次。不过目前该软件的局限性还很大,只能完成一些简单的修复。

该项目使用深度完全卷积神经网络(deep fully convolutional neural network),参照了英伟达在今年4月前发布的一篇论文。当然,英伟达原文的目的可不是用来做羞羞的事情,而是为了复原画面被单色条带遮挡的问题。

从实际效果来看,复原后的图片涂抹痕迹仍然比较明显,不过处理线条比较简单的漫画可以说是绰绰有余。
2、适用范围
DeepCreamPy仅适用于薄码,如果马赛克太大太厚,去码可能会失效。另外,它对真人图片无效。如果你非要尝试,可以看一下强行使用的效果:

而且DeepCreamPy目前的版本还不能完全自动处理图片,需要用Photoshop首先对马赛克部分进行手动预处理。
3、使用方法
第一步:安装程序
1、如果你是64位Windows用户,恭喜你可以直接下载exe程序
下载地址:https://github.com/deeppomf/DeepCreamPy/releases/latest
2、否则需要自己编译,编译代码需要一下组件:
- Python 3.6
- TensorFlow 1.10
- Keras 2.2.4
- Pillow
- h5py
请注意软件版本,Windows上的TensorFlow不兼容Python 2,也不兼容Python 3.7。
代码如下:
- import numpy as np
- from PIL import Image
- import os
-
- from copy import deepcopy
-
- import config
- from libs.pconv_hybrid_model import PConvUnet
- from libs.utils import *
-
- class Decensor:
-
- def __init__(self):
- self.args = config.get_args()
- self.is_mosaic = self.args.is_mosaic
-
- self.mask_color = [self.args.mask_color_red/255.0, self.args.
- mask_color_green/255.0, self.args.mask_color_blue/255.0]
-
- if not os.path.exists(self.args.decensor_output_path):
- os.makedirs(self.args.decensor_output_path)
-
- self.load_model()
-
- def get_mask(self, colored):
- mask = np.ones(colored.shape, np.uint8)
- i, j = np.where(np.all(colored[0] == self.mask_color, axis=-1))
- mask[0, i, j] = 0
- return mask
-
- def load_model(self):
- self.model = PConvUnet()
- self.model.load(
- r"./models/model.h5",
- train_bn=False,
- lr=0.00005
- )
-
- def decensor_all_images_in_folder(self):
- #load model once at beginning and reuse same model
- #self.load_model()
- color_dir = self.args.decensor_input_path
- file_names = os.listdir(color_dir)
-
- #convert all images into np arrays and put them in a list
- for file_name in file_names:
- color_file_path = os.path.join(color_dir, file_name)
- color_bn, color_ext = os.path.splitext(file_name)
- if os.path.isfile(color_file_path) and color_ext.casefold() == ".png":
- print("-----------------------------------------------------------
- ---------------")
- print("Decensoring the image {}".format(color_file_path))
- colored_img = Image.open(color_file_path)
- #if we are doing a mosaic decensor
- if self.is_mosaic:
- #get the original file that hasn't been colored
- ori_dir = self.args.decensor_input_original_path
- #since the original image might not be a png, test multiple file formats
- valid_formats = {".png", ".jpg", ".jpeg"}
- for test_file_name in os.listdir(ori_dir):
- test_bn, test_ext = os.path.splitext(test_file_name)
- if (test_bn == color_bn) and (test_ext.casefold() in valid_formats):
- ori_file_path = os.path.join(ori_dir, test_file_name)
- ori_img = Image.open(ori_file_path)
- # colored_img.show()
- self.decensor_image(ori_img, colored_img, file_name)
- break
- else: #for...else, i.e if the loop finished without encountering break
- print("Corresponding original, uncolored image not found in {}.
- ".format(ori_file_path))
- print("Check if it exists and is in the PNG or JPG format.")
- else:
- self.decensor_image(colored_img, colored_img, file_name)
- print("--------------------------------------------------------------------------")
-
- #decensors one image at a time
- #TODO: decensor all cropped parts of the same image in a batch (then i need
- input for colored an array of those images and make additional changes)
- def decensor_image(self, ori, colored, file_name):
- width, height = ori.size
- #save the alpha channel if the image has an alpha channel
- has_alpha = False
- if (ori.mode == "RGBA"):
- has_alpha = True
- alpha_channel = np.asarray(ori)[:,:,3]
- alpha_channel = np.expand_dims(alpha_channel, axis =-1)
- ori = ori.convert('RGB')
-
- ori_array = image_to_array(ori)
- ori_array = np.expand_dims(ori_array, axis = 0)
-
- if self.is_mosaic:
- #if mosaic decensor, mask is empty
- # mask = np.ones(ori_array.shape, np.uint8)
- # print(mask.shape)
- colored = colored.convert('RGB')
- color_array = image_to_array(colored)
- color_array = np.expand_dims(color_array, axis = 0)
- mask = self.get_mask(color_array)
- # mask_reshaped = mask[0,:,:,:] * 255.0
- # mask_img = Image.fromarray(mask_reshaped.astype('uint8'))
- # mask_img.show()
-
- else:
- mask = self.get_mask(ori_array)
-
- #colored image is only used for finding the regions
- regions = find_regions(colored.convert('RGB'))
- print("Found {region_count} censored regions in this image!".format
- (region_count = len(regions)))
-
- if len(regions) == 0 and not self.is_mosaic:
- print("No green regions detected!")
- return
-
- output_img_array = ori_array[0].copy()
-
- for region_counter, region in enumerate(regions, 1):
- bounding_box = expand_bounding(ori, region)
- crop_img = ori.crop(bounding_box)
- # crop_img.show()
- #convert mask back to image
- mask_reshaped = mask[0,:,:,:] * 255.0
- mask_img = Image.fromarray(mask_reshaped.astype('uint8'))
- #resize the cropped images
- crop_img = crop_img.resize((512, 512))
- crop_img_array = image_to_array(crop_img)
- crop_img_array = np.expand_dims(crop_img_array, axis = 0)
- #resize the mask images
- mask_img = mask_img.crop(bounding_box)
- mask_img = mask_img.resize((512, 512))
- # mask_img.show()
- #convert mask_img back to array
- mask_array = image_to_array(mask_img)
- #the mask has been upscaled so there will be values not equal to 0 or 1
-
- mask_array[mask_array > 0] = 1
-
- if self.is_mosaic:
- a, b = np.where(np.all(mask_array == 0, axis = -1))
- print(a, b)
- coords = [coord for coord in zip(a,b) if ((coord[0] + coord[1]) % 2
- == 0)]
- a,b = zip(*coords)
-
- mask_array[a,b] = 1
- # mask_array = mask_array * 255.0
- # img = Image.fromarray(mask_array.astype('uint8'))
- # img.show()
- # return
-
- mask_array = np.expand_dims(mask_array, axis = 0)
-
- # Run predictions for this batch of images
- pred_img_array = self.model.predict([crop_img_array, mask_array, mask_array])
-
- pred_img_array = pred_img_array * 255.0
- pred_img_array = np.squeeze(pred_img_array, axis = 0)
-
- #scale prediction image back to original size
- bounding_width = bounding_box[2]-bounding_box[0]
- bounding_height = bounding_box[3]-bounding_box[1]
- #convert np array to image
-
- # print(bounding_width,bounding_height)
- # print(pred_img_array.shape)
-
- pred_img = Image.fromarray(pred_img_array.astype('uint8'))
- # pred_img.show()
- pred_img = pred_img.resize((bounding_width, bounding_height),
- resample = Image.BICUBIC)
-
- pred_img_array = image_to_array(pred_img)
-
- # print(pred_img_array.shape)
- pred_img_array = np.expand_dims(pred_img_array, axis = 0)
-
- # copy the decensored regions into the output image
- for i in range(len(ori_array)):
- for col in range(bounding_width):
- for row in range(bounding_height):
- bounding_width_index = col + bounding_box[0]
- bounding_height_index = row + bounding_box[1]
- if (bounding_width_index, bounding_height_index) in region:
- output_img_array[bounding_height_index][bounding_
- width_index] = pred_img_array[i,:,:,:][row][col]
- print("{region_counter} out of {region_count} regions decensored."
- .format(region_counter=region_counter, region_count=len(regions)))
-
- output_img_array = output_img_array * 255.0
-
- #restore the alpha channel if the image had one
- if has_alpha:
- output_img_array = np.concatenate((output_img_array, alpha_channel),
- axis = 2)
-
- output_img = Image.fromarray(output_img_array.astype('uint8'))
-
- #save the decensored image
- #file_name, _ = os.path.splitext(file_name)
- save_path = os.path.join(self.args.decensor_output_path, file_name)
- output_img.save(save_path)
-
- print("Decensored image saved to {save_path}!".format(save_path=save_path))
- return
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- decensor = Decensor()
- decensor.decensor_all_images_in_folder()
注意:运行Demo需要翻墙下载模型,这里为了方便小伙伴,我已经下载完毕:https://download.csdn.net/download/m0_38106923/10798221
第二步:手动处理黑条遮挡和马赛克遮挡
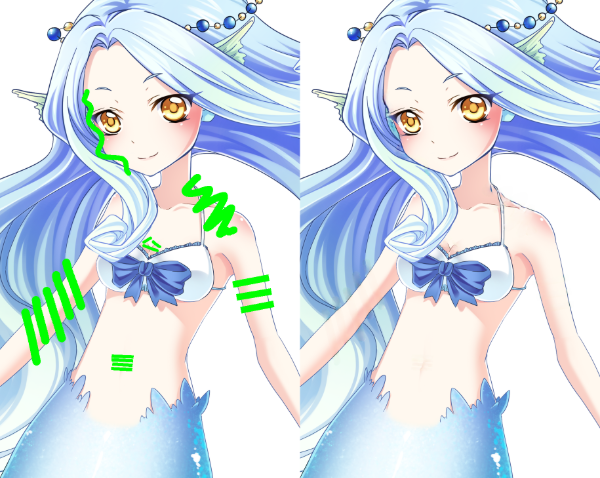
首先打开Photoshop或者其它图片处理器。对于单色条遮住人物敏感部位的情况,使用纯绿色(色号#00FF00#)预处理图片,以绿条取代图片中的黑条。
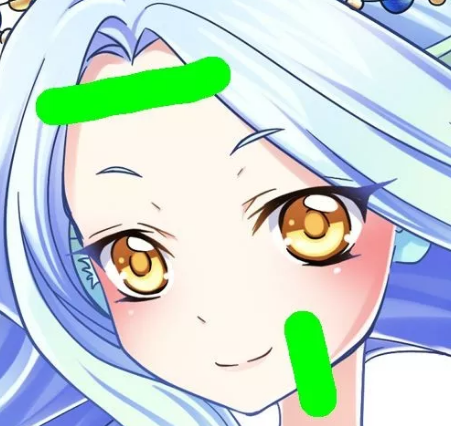

强烈建议使用铅笔而不是毛刷工具,如果使用毛刷,请一定要关闭抗锯齿功能。或者用魔棒选中马赛克区域,再用油漆桶上色。这里我给各位分享一个Python编写的处理工具,代码比较长,所以和模型文件放在一起,各位可以尝试下载。
最后将处理的文件以PNG格式存储在软件的”decensor_input”文件夹中。如果敏感部位不是黑条,而是马赛克,还需要将未上色的原始图片放入”decensor_input_original” 文件夹中,并确保其文件名和放在”decensor_input”中的预处理图片文件名相同
第三步:运行去马赛克软件
1、64位Windows用户下载程序的exe后,双击软件即可
2、自行编译项目的用户,需要执行以下两个命令
对于黑条遮挡的图片,输入以下命令:
$ pythondecensor.py
对于马赛克遮挡的图片,输入以下命令:
$ python decensor.py —is_mosaic=True
注意事项
如果你图片处理后成了这样:

一定是你处理的姿势不对,请注意不要犯以下两种错误:

第一幅图中,图片马赛克区域没有完全涂满;第二幅图中,由于开启了抗锯齿功能,导致马赛克边缘区域不是纯绿色填充,请关闭抗锯齿功能!!
关注公众号,发送关键字:Java车牌识别,获取项目源码。



 个人中心
个人中心 退出
退出




 分类导航
分类导航